INTRODUCTION
Welcome science enthusiasts and fellow learners! Through my blog, Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science today I am thrilled to dive into the fascinating realm of chemistry with you. Whether you’re a Class 10 student or someone with a curious mind seeking a refresher, these comprehensive notes for 2024 are here to make the world of Chemical Reactions and Equations not only understandable but exciting also.
Buckle up now as I am going to unravel the mysteries of chemical transformations, explore the dance of elements, and decode the language of equations.

Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Main Points to remember about Chemical Reactions
- The processes in which new substances with new properties are formed are called Chemical reactions.
- Chemical reactions involve chemical changes, and a rearrangement of atoms takes place between the reacting substances to form new substances which have entirely different properties.
- Only a rearrangement of atoms takes place in a chemical reaction, atoms of one element do not change into those of another element.
Reactants and Products of Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
(i) Reactants are the substances which take part in a chemical reaction.
(ii) Products are the new substances produced as a result of chemical reaction .
Chemical reaction of ‘magnesium’ with the ‘oxygen’ of air —
Magnesium ribbon burns in air with a white flame and a white powder is formed which is called magnesium oxide
2Mg(s) + O2(g)—-2MgO(s)
In this reaction, magnesium combines with oxygen (present in air) to form magnesium oxide:
Why is the magnesium ribbon cleaned by rubbing with a sandpaper before burning in air?
There is a coating of ‘magnesium oxide’ on the surface of the magnesium ribbon which we use. It is formed by the slow action of oxygen of air on it. So, magnesium ribbon is cleaned by rubbing with a sandpaper before burning in air, By doing so, we can remove the protective layer of magnesium oxide from the surface of magnesium ribbon. On heating, this magnesium ribbon can readily combine with the oxygen of air.
Chemical changes involve chemical reactions:
Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Important Examples
Souring of milk – When milk is left at room temperature during summer, it becomes sour in taste.
Formation of curd from milk,
Cooking of food,
Digestion of food in our body,
Process of respiration,
Fermentation of grapes,
Rusting of iron -When iron is left exposed to humid atmosphere it undergoes rusting.
Burning of fuels (like wood, coal, kerosene, petrol and LPG),
Burning of candle wax, and Ripening of fruits,
CHARACTERISTICS OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
The important characteristics of chemical reactions are :
(i) Evolution of a gas,
(ii) Formation of a precipitate,
(iii) Change in colour,
(iv) Change in temperature, and
(v) Change in state
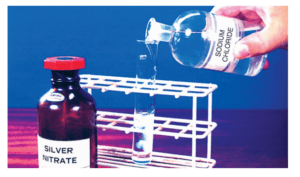
Examples to show all the characteristics of chemical reactions: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
1. Evolution of a Gas
Examples-
When dilute sulphuric acid is put into zinc granules , hydrogen gas is released.
Magnesium reacts with a dilute acid (e.g. dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulphuric acid) to produce hydrogen gas.
When sodium carbonate reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid ,carbon dioxide gas is evolved.
2. Formation of a Precipitate
(Precipitation is the formation of an insoluble product.)
In case of some chemical reactions, a precipitate is formed.
Examples
when a solution of lead nitrate is added to potassium iodide solution, a precipitate of lead iodide is formed which is of yellow colour.
If dilute sulphuric acid is added to barium chloride solution, a precipitate of barium sulphate is formed which is white in colour.
In some cases an insoluble product (called precipitate) is formed by the reaction between solutions of reactants (or a solution and a gas).
The physical state of precipitate is indicated by the symbol (s) since this insoluble product (precipitate) is a solid substance,
For example, when calcium hydroxide solution (lime water) reacts with carbon dioxide gas, a white precipitate of calcium carbonate is formed along with water.
Ca(OH)2 (aq) + CO2 (g)– CaCO3 (s) + H2O (1)
Calcium hydroxide Calcium carbonate (White ppt.)
The word ‘precipitate’ is also written as ‘ppt’ (in short form)
3. Change in Colour
Some chemical reactions are characterised by a change in colour.
For example,
- When potassium permanganate solution reacts with citric acid, the purple
colour of potassium permanganate solution disappears .
So, we can say that the chemical reaction between citric acid and potassium permanganate solution is characterised by a change in colour (from purple to colourless) - When acidified potassium dichromate solution reacts with sulphur dioxide gas, the orange colour of potassium dichromate solution changes to green.
4. Change in Temperature
Some chemical reactions are characterized by a change in temperature.
For example,
1).When quicklime reacts with water, then slaked lime is formed and a lot of heat energy is produced.
Above reaction is an exothermic reaction because heat is evolved.
2).The chemical reaction between barium hydroxide and ammonium chloride to form barium chloride, ammonia and water is characterised by a change in temperature (which is fall in temperature). It is an endothermic reaction (which means heat absorbing reaction).
on the basis of heat changes, there are two types of reactions-
Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science: Exothermic reactions and Endothermic reactions.
Exthermic reactions.
Those reactions in which heat is evolved are known as exothermic reactions.
For example,
(i) when carbon burns in oxygen to form carbon dioxide, a lot of heat is produced in this reaction :
C (s) + O2 (g)—CO2 (g) + Heat
Above reaction is an exothermic reaction because heat is evolved here.
An exothermic reaction is indicated by writing “+ Heat” or “+ Heat energy” or just “+ Energy” on the products’ side of an equation (as shown in the above equation).
(II) When natural gas burns in the oxygen of air, it forms carbon dioxide and water vapour, along with large amount of heat energy.
This can be written as :
CH4 (g) + 2O2 (g)– CO2 (g) + 2H2O (g) + Heat energy
(Methane)
(Natural gas)
Above reaction is an exothermic reaction because heat is produced here.
Best Reference Book for CBSE Science 10




More Examples of Exothermic Reactions: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
(i)Combustion of fuels such as wood, coal, kerosene, petrol and diesel, are all exothermic reactions (because all these reactions produce heat energy).
(ii)Even the combustion of food (like glucose) in our body during respiration is an exothermic reaction. .
(iii)During digestion, starch carbohydrate is broken down into a simple carbohydrate called glucose. In the cells of our body, this glucose undergoes slow combustionand combines with oxygen to produce energy, This process is called respiration.
(iv)During respiration, glucose combines with oxygen in the cells of our body to form carbon dioxide and water along with the production of energy :
C6H12O6 (aq) + 6O2 (g) –6CO2 (g) + 6H2O (l) + Energy
(Glucose)
Respiration is an exothermic process because energy is produced during this process (as shown by the above equation).
(v)The burning of a magnesium wire in air to form magnesium oxide is an exothermic reaction because heat and light energy are given out during this reaction.
(vi)The decomposition of vegetable matter into compost is also an example of an exothermic process (because heat energy is evolved during this process).
Endothermic reactions: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Endothermic reactions are the reactions in which heat is absorbed.
For example, nitrogen and oxygen combine to form nitrogen monoxide when they are heated to a very high temperature (of about 3000°C) . A lot of heat is absorbed they in this reaction :
N2 (g) + O2 (g) + Heat–2NO (g)
(Nitrogen monoxide )
The reaction between nitrogen and oxygen to form nitrogen monoxide is an endothermic reaction because heat is absorbed in this reaction.
An endothermic reaction is usually indicated by writing “+ Heat” or “+ Heat energy ” or just “+ Energy” on the reactants’ side of an equation
The reaction in which nitrogen and oxygen (of air) combine to form nitrogen monoxide takes place inside the engines of motor vehicles.
More Examples of Endothermic Reaction: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
All the decomposition reactions are endothermic reactions because these reactions need energy (in the form of heat, light or electricity).
For example,
(i)When calcium carbonate is heated, it decomposes to form calcium oxide and carbon dioxide :
CaCO3 (s) + Heat– CaO (s) + CO2 (g)
(Calcium carbonate)
Above reaction is an endothermic reaction because heat energy is absorbed in this reaction.
(ii) Photosynthesis is an endothermic reaction.
This is because sunlight energy is absorbed during the process of photosynthesis by green plants.
(iii)The electrolysis of water to form hydrogen and oxygen is also an endothermic reaction because electric energy is absorbed during this reaction.
It is clear from this discussion that energy can be given out or absorbed in chemical reactions in the form of heat, light or electricity.
5. Change in State
A change of state takes place in some chemical reactions.
For example, water and carbon dioxide are formed when wax is burned.
So, the physical state changes from solid to liquid and gas.
Here, wax is a solid, water is a liquid but carbon dioxide is a gas.

CHEMICAL EQUATIONS: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Chemical equation is a way of representing a chemical reaction with the help of symbols and formulae of the substances.
Example: A + B → C + D
In the above equation, A and B react with each other. So, they are called reactants .
C and D are produced when A and B react with each other. So, C and D are called the products.
Reactants are the substances which combine or react.
Products are the new substances produced in a reaction.
Balanced and Unbalanced Chemical Equations: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Balanced Chemical Equation
The chemical equation in which the number of atoms of each element is equal on both sides, is called a Balanced Chemical Equation.
Example: Zn + H2SO4 → ZnSO4 + H2
This equation is a Balanced Chemical Equation because the number of zinc, hydrogen and sulphate are equal on both sides.
Unbalanced Chemical Equation: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
The chemical equation in which the number of atoms of each element is not equal on both sides, is called an Unbalanced Chemical Equation.
Example: Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
It is an unbalanced chemical equation because number of atoms of elements are not equal on both the sides of the reaction.
Balancing a Chemical Equation: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Balancing of a chemical equation means making the number of atoms of each element equal in reactants and products.
How to Balance a Chemical Equation: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
We consider the chemical equation-
Fe + H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
To balance the given equation (or any chemical equation) we have to follow the following steps-
First of all , we write the number of atoms of elements present in reactants and in products in a table which is as follows-
| Name of atom | No. of atoms in the reactant | No. of atoms in the product |
| Iron | 1 | 3 |
| Hydrogen | 2 | 2 |
| Oxygen | 1 | 4 |
To balance the oxygen, one needs to multiply the oxygen on the LHS by 4, so that, the number of oxygen atoms becomes equal on both sides.
Fe + 4 × H2O → Fe3O4 + H2
We observe that the number of hydrogen atoms becomes 8 on the LHS, which is more than that on the RHS. To balance it, we need to multiply the hydrogen on the RHS by 4.
Fe + 4 × H2O → Fe3O4 + 4 × H2
Now, the number of atoms of both oxygen and hydrogen becomes equal on both sides.
But, the number of iron atoms is one on the LHS and it is three on the RHS.
To balance it, We have to multiply the iron on the LHS by 3.
3 × Fe + 4 × H2O → Fe3O4 + 4 × H2
Finally, the number of atoms of each element becomes equal on both sides. In this way, the above equation becomes a balanced chemical equation.
| Name of atom | No. of atoms in the reactant | No. of atoms in the product |
| Iron | 3 | 3 |
| Hydrogen | 8 | 8 |
| Oxygen | 4 | 4 |
Balanced chemical equation can be written as –
3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2.
Ways to make Chemical Equations More Informative
Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
(1).By writing the “physical states” of the reactants and products. as follows-
- Solid state by symbol (s)
- Liquid state symbol (l)
- Aqueous solution (solution made in water) by symbol (aq)
- Gaseous state by symbol (g)
(2) By writing the “heat changes” that takes place in the chemical reaction.
An exothermic reaction is indicated by writing “+ Heat” or “+ Heat energy” or just “+ Energy” on the products’ side of an equation (as shown in the above equation).
(3)By writing the “conditions” under which the reaction takes place.
We generally write the condition of the reaction above and/or below the arrow of a chemical equation.
The heat sign delta () is put over the arrow of the equation. If heat is required for a reaction to take place.
The symbol or formula of the catalyst is written above or below the arrow sign in the equation, if the reaction occurs in the presence of a catalyst.
WATCH THESE VIDEOS (For Better Concept)
TYPES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS
Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Combination reactions,
Decomposition reactions,
Displacement reactions,
Double displacement reactions, and
Oxidation and Reduction reactions
COMBINATION REACTIONS: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Combination reactions are the reactions in which two or more substances combine to form a single substance.
In this type of reaction–
two or more elements can combine to form a compound.
two or more compounds can combine to form a new compound.
or an element and a compound can combine to form a new compound.
Examples of combination reactions.
Example 1.
When heated, Magnesium combines with oxygen to form magnesium oxide.
2Mg (s) + O2 (g)— 2MgO (s)
Here, two elements, magnesium and oxygen, combine to form a single compound( magnesium oxide).
So, this is a combination reaction.
Example 2.
Carbon combines with oxygen when carbon is burnt in oxygen (air) to give carbon dioxide.
C (s) + O2(g) → CO2(g)
Carbon + Oxygen → Carbon dioxide
Calcium oxide (lime or quicklime) reacts vigorously with water. As a result, calcium hydroxide (slaked lime) is formed. Clearly, it is a combination reaction.
CaO (s) + H2O (l) — Ca(OH)2 (s)
This is a combination reaction in which two compounds, calcium oxide and water, combine to form a single compound calcium hydroxide.
Main Points Related to the Above Reaction
When calcium oxide reacts with water to form calcium hydroxide (or slaked lime), A large amount of heat is released.
A white solid called calcium hydroxide (or slaked lime) is formed with the evolution of heat when calcium oxide reacts with water vigorously.
When applied to the walls, calcium hydroxide solution, reacts slowly with the carbon dioxide gas present in air . As a result, a thin shining layer of calcium carbonate is deposited on the walls of the house.
Ca(OH)2 (aq) + CO2 (g)–CaCO3 (s) + H2O (l)
DECOMPOSITION REACTIONS: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Decomposition reactions are the reactions in which a compound splits up into two or more simpler substances.
This can be done by applying heat, light or electricity which provide energy to break a compound into two or more simpler compounds.
A general decomposition reaction can be represented as follows :
AB → A + B
Examples:
(i)When heated, calcium carbonate decomposes into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide.

(ii) When ferrous sulphate is heated strongly, it decomposes to form ferric oxide, sulphur dioxide and sulphur trioxide .

Type of Decomposition Reaction: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Thermal Decomposition:
That decomposition reaction, which is carried out by heating, is called ‘thermal decomposition’.
Example 1.
When heated, calcium carbonate splits into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide
It is a thermal decomposition because it is carried out by heating.

Example 2.
Potassium chlorate decomposes to give potassium chloride and oxygen when it is heated in the presence of manganese dioxide catalyst.
2KClO3 (s)+ Heat — 2KCl (s) + 3O2 (g)
Potassium chlorate Potassium chloride
Electrolytic Decomposition: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Electrolytic Decomposition are the reactions in which compounds decomposes into simpler substances when electricity is passed through them. This reaction is also called Electrolysis.
Example
Acidified water decomposes to give hydrogen gas and oxygen gas When electric current is passed through it.
This reaction can be represented as :
2H2O (l) — Electricity– 2H2 (g) + O2 (g)
Water Hydrogen Oxygen
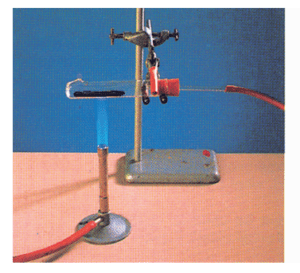
Photolytic Decomposition Reaction or Photolysis
Photolytic Decomposition Reaction or Photolysis is that decomposition reaction in which a compound decomposes because of sunlight.
As a result of the decomposition of silver chloride into silver and chlorine by light , the white colour of silver chloride changes to greyish white because of the formation of silver metal.
This reaction is used in black and white photography.

We notice a similar reaction when silver bromide is exposed to sumlight.

Pale yellow colour of silver bromide changes to greyish white due to the formation of silver metal in the above reaction. The decomposition of silver bromide is caused by light( sunlight or bulb light).
This decomposition of silver bromide is also used in black and white photography.
(iii) Displacement Reaction: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Displacement Reactions or Substitution Reaction or Single Displacement reactions are the chemical reactions in which a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from a compound.
Displacement reaction can be represented as follows.
A + BC → AC + B
(Here, we assume that A is more reactive than B).
Examples:
1) When zinc reacts with hydrochloric acid, it gives hydrogen gas and zinc chloride.
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
2) Zinc displaces copper from copper sulphate solution because zinc is more reactive than copper. As a result, zinc sulphate and copper metal are formed.
Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
In the above reaction, the blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades due to the formation of zinc sulphate (which is colourless). Moreover, a red-brown deposit of copper metal is also formed.
(iv) Double Displacement Reaction: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Double Displacement Reactions are the reactions in which ions are exchanged between two reactants to form new compounds.
AB + CD → AC + BD
Examples:
(i)When the solution of barium chloride reacts with the solution of sodium sulphate, white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed along with sodium chloride.
BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) → BaSO4(s) (Precipitate) + 2NaCl(aq)
(ii)Sodium hydroxide (a base) reacts with hydrochloric acid to form sodium chloride and water . There is an exchange of ions between NaOH and HCl .
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
Important Note
Double Displacement Reaction is also called precipitation reaction because precipitate is formed in this type of reaction.
Neutralization reactions are also double displacement reaction.
Precipitation Reaction: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Precipitation Reaction is the reaction in which precipitate is formed by the mixing of the aqueous solution of two salts.
Example
The reaction between barium chloride solution and sodium sulphate solution to form barium sulphate precipitate (along with sodium chloride solution) is an example of a precipitation reaction.
BaCl2 (aq) + CuSO4 (aq)— BaSO4 (s) + CuCl2 (aq)
Barium chloride Barium sulphate (White ppt.)
Neutralization Reaction: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Neutralization Reaction is the reaction in which an acid and a base react with each other to form salt and water in which they neutralise each other to produce a neutral compound (salt).
Example:-
![]()
In general, a neutralization reaction can be written as –
Base + Acid → Salt + Water
(v) Oxidation and Reduction Reactions: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Oxidation
Addition of oxygen (or any non-metallic element ) to a compound or removal of hydrogen (or metallic element) from a compound is called Oxidation.

Reduction
Addition of hydrogen (or any metallic element) to a compound or removal of oxygen (or any non-metallic element) from a compound is called Reduction.

Oxidizing agent
- Oxidising agent is the substance which is reduced.
- It is the substance which gives oxygen for oxidation.
- It is the substance which removes hydrogen.
In the above oxidation reaction, CuO is an Oxidising agent.
Reducing agent
- Reducing agent is. the substance which gets oxidised.
- Reducing agent is the substance which gives hydrogen for reduction.
- It is the substance which removes oxygen from a substance during reduction.
In the above oxidation reaction, H2 is a reducing agent.
Redox reaction: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
If oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously, the reaction is called Redox reaction
Example 1.
Copper oxide reacts with hydrogen to give copper metal and hydrogen gas.
CuO + H2 → Cu + H2O
Here, Oxygen is being removed from copper oxide (CuO). In this way,copper oxide is being reduced to copper.
Also, Oxygen is being added to hydrogen. Clearly, hydrogen is being oxidised to water.
Hydrogen is the reducing agent here because H2 is getting oxidised. Moreover, Hydrogen is responsible for removing oxygen from copper oxide.
Copper oxide is the oxidising agent because it is getting reduced . Moreover CuO is giving the oxygen required for the oxidation of hydrogen.
Conclusions about the above oxidation-reduction reaction :-
(i) Substance oxidised : H2
(ii) Substance reduced : CuO
(iii) Oxidising agent : CuO
(iv) Reducing agent : H2
Example 2.
Hydrogen sulphide reacts with chlorine to give sulphur and hydrogen chloride.
H2S + Cl2 — S + 2HCl
Here, Hydrogen sulphide is being oxidised to sulphur because hydrogen is being removed from hydrogen sulphide. So, hydrogen sulphide is the reducing agent. Moreover, hydrogen sulphide is supplying hydrogen to chlorine for reduction,
Also, Chlorine is the oxidising agent in this reaction. As Cl2 is changing into HCl, hydrogen is being added to chlorine. Clearly, chlorine is being reduced to hydrogen chloride. Moreover, chlorine is removing hydrogen from hydrogen sulphide,
Conclusions about the above oxidation-reduction reaction :-
(i) Substance oxidised : H2S
(ii) Substance reduced : Cl2
(iii) Oxidising agent : Cl2
(iv) Reducing agent : H2S
Example 3.
When manganese dioxide reacts with hydrochloric acid, then manganese dichloride, chlorine
and water are formed :
MnO2 + 4HCl — MnCl2 + Cl2 + 2H2O
Manganese Manganese
dioxide dichloride
Here , Manganese dioxide (MnO2) is being reduced to manganese dichloride (MnCl2) and Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is being oxidised to chlorine (Cl2). So .In this reaction, manganese dioxide (MnO2) is the oxidising agent whereas hydrochloric acid (HCl) is the reducing agent.
Another Concept of oxidation and reduction–
(i) Oxidation is the addition of non-metallic element or removal of metallic element.
(ii) Reduction is the addition of metallic element or removal of non-metallic element.
EFFECTS OF OXIDATION REACTIONS IN EVERYDAY LIFE: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
1.Corrosion of metals and
2. Rancidity of food.
Please note that the oxidation involved in the corrosion of metals as well as rancidity of food is caused naturally by the oxygen present in air.
Corrosion: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Corrosion is the process by which metals are eaten up gradually by the action of air, moisture or a chemical (such as an acid).
Rusting of iron metal is the most common form of corrosion.
Iron is covered with a red-brown flaky substance called ‘rust’, when any iron object is left in damp air for a considerable time, This is called rusting of iron.
During the corrosion of iron (or rusting of iron), iron metal is oxidised by the oxygen of air in the presence of water (moisture) to form hydrated iron (III) oxide called rust .
The rusting of iron is a redox reaction. Rusting involves unwanted oxidation of iron metal which occurs in nature on its own.
Rust is a soft and porous substance which gradually falls off from the surface of an iron object, and then the iron below starts rusting.
If not prevented in time, the rust eats up the whole iron object. Iron and steel objects and structures such as railings, car bodies, bridges and ships, etc. are weakened by Corrosion .A lot of money has to be spent every year to prevent the corrosion of iron and steel objects, and to replace the damaged iron and steel structures.
Rancidity: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
If the food materials prepared in fats and oils are kept for a long time, they start giving unpleasant smell and taste.. Food materials containing fat and oil which give unpleasant smell and taste are said to have become rancid.
Fats and oils present in food materials get oxidised by the oxygen (of air). The condition produced by the oxidation of fats and oils is marked by unpleasant smell and taste. This process is called rancidity. Rancidity spoils the food materials prepared in fats and oils and makes them unfit for eating.
Ways to prevent the rancidity of food —
1. By adding antioxidants to foods containing fats and oils.
Antioxidant is a substance (or chemical) which prevents oxidation. When antioxidants are added to foods, then the fats and oils present in them do not get oxidised easily and hence do not turn rancid. In this way, foods can be kept in good condition for a much longer time. BHA (Butylated Hydroxy-Anisole) and BHT (Butylated Hydroxy-Toluene) are two common antioxidants, which are used to prevent rancidity.
2. By packaging fat and oil containing foods in nitrogen gas, rancidity can be prevented. There is oxidation , when the packed food is surrounded by an unreactive gas nitrogen.
To prevent the chips from being oxidised and turn rancid, the manufacturers of potato chips (and other similar food products) fill the plastic bags containing chips with nitrogen gas.
3. By keeping food in a refrigerator, Rancidity can be retarded. Oxidation of fats and oils is slowed down due to low temperature when the food is kept in a refrigerator. In this way, rancidity can be retarded.
4. When food is stored in air-tight containers, then there is little exposure to oxygen of air. Hence, rancidity can be retarded by storing food in air-tight containers.
Due to reduced exposure to oxygen, the oxidation of fats and oils present in food is slowed down and hence the development of rancidity is retarded.
5. By storing foods away from light, rancidity can be retarded to a great extent. It is due to the fact that oxidation of fats and oils (present in food) is slowed down in the absence of light, hence the development of rancidity is retarded.
FAQs: Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science
Q(1). How can you identify a chemical reaction?
Answer- Signs of a chemical reaction include the formation of a precipitate, evolution of gas, change in color, change in temperature, and the production of light. These observations help in identifying a chemical change.
Q(2). What are reactants and products in a chemical reaction?
Answer- Reactants are the substances present at the beginning of a chemical reaction, and products are the substances formed as a result of the reaction. Reactants transform into products during the reaction.
Q(3). How are chemical equations written?
Answer- Chemical equations are written by representing reactants on the left side and products on the right side, separated by an arrow. The chemical formulas and coefficients indicate the quantities of each substance involved.
Q(4). What is the law of conservation of mass?
Answer- The law of conservation of mass states that the total mass of the reactants in a chemical reaction is equal to the total mass of the products. Mass can neither be created nor destroyed during a chemical reaction.
Q(5). How do you balance a chemical equation?
Answer- Balancing a chemical equation involves adjusting the coefficients of reactants and products to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides. This maintains the law of conservation of mass.
Q(6). What is a catalyst in a chemical reaction?
Answer – A catalyst is a substance that speeds up a chemical reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway with lower activation energy. It is not consumed in the reaction and does not undergo permanent changes.
Q(7). Can you provide examples of everyday chemical reactions?
Answer- Examples include rusting of iron, digestion of food, burning of a candle, baking a cake, and photosynthesis. These everyday processes involve chemical reactions that are essential for various natural and human-made activities.
PLEASE ALSO READ-
https://pcmconceptclear.com/best-book-for-science-class-10-cbse/
https://pcmconceptclear.com/science-class-10-control-and-coordination/
https://pcmconceptclear.com/science-class-10-light-reflection-and-refraction/
https://pcmconceptclear.com/science-class-10-life-processes/
https://pcmconceptclear.com/science-class-10-acids-bases-and-salts/
https://pcmconceptclear.com/class-10-chemical-reactions-and-equations/
https://pcmconceptclear.com/acids-bases-salts-most-imp-qa
YOU TUBE VIDEO SUPPORT
Source: Home School

12 thoughts on “Chemical Reactions And Equations Class 10 Science Notes (2025-26)”